Bank Deposits:
Bank Deposits: Safeguarding Your Money and Earning Interest
Bank deposits are a cornerstone of personal finance, serving as secure repositories for your hard-earned money while offering opportunities for modest returns on your funds. Understanding the various types of bank deposits and their distinctive features is essential for making informed financial decisions.
Types of Bank Deposits:
- Demand Deposits (Checking Accounts):
Definition: Demand deposits, commonly known as checking accounts, are the most accessible form of bank deposit. These accounts provide you with the flexibility to withdraw funds at your convenience without any significant restrictions.
Characteristics:
- Accessible through checks, debit cards, or electronic transfers.
- No fixed maturity date; funds are available on demand.
- Typically offer minimal to no interest.
Advantages:
- Exceptional liquidity, ideal for everyday transactions.
- Convenient access to funds for bill payments, purchases, and ATM withdrawals.
Disadvantages:
- Generally, lower interest rates when compared to other deposit types.
- May incur monthly maintenance fees.
- Time Deposits (Savings Accounts and Certificates of Deposit – CDs):
Explanation: Time deposits involve depositing a specific sum of money for a predetermined period, such as several months or years. Although less liquid than demand deposits, they compensate for this with higher interest rates.
Examples:
- Savings Accounts: Offer moderate interest rates and some liquidity, allowing limited withdrawals without penalties.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Feature higher interest rates but require the deposit to remain untouched for a specified term (e.g., 6 months, 1 year, or longer).
Benefits:
- Typically yield higher interest rates compared to demand deposits.
- Encourage disciplined saving by discouraging frequent withdrawals.
Drawbacks:
- Liquidity is limited; early withdrawals from CDs can result in penalties.
- Returns may be lower compared to certain investment options.
- Savings Deposits:
Definition: Savings deposits are tailored to promote a culture of saving. They are often offered by banks and credit unions with specific terms and conditions to help individuals set money aside over time.
Characteristics:
- Generally feature lower minimum balance requirements compared to time deposits.
- Allow a limited number of monthly withdrawals or transfers.
- Variable interest rates, which may be higher than demand deposit rates.
Features and Limitations:
- Primarily designed for long-term savings objectives.
- Examples include regular savings accounts and high-yield savings accounts.
- May offer features like overdraft protection and automated transfers.
Advantages:
- Encourage disciplined saving habits.
- Moderate interest rates are potentially higher than those offered by demand deposits.
Disadvantages:
- Limited liquidity for frequent withdrawals.
- Variable interest rates may fluctuate over time.
Recurring Deposit:
Recurring Deposit [RD] is a special kind of Bank Term Deposit offered by banks in India which help people with regular incomes to deposit a fixed amount every month into their Recurring Deposit account and earn interest at the rate applicable to Fixed Deposits.

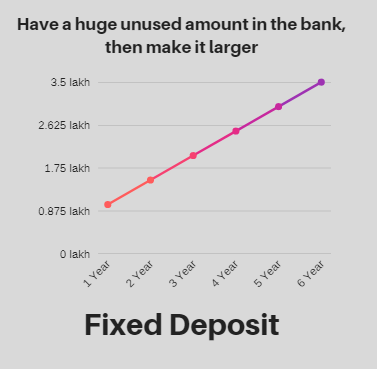
Fixed deposit:
Fixed deposits [FD] is a type of Bank deposit offered by the bank in helping the investors in getting a higher rate of interest, than regular savings account on the maturity date for which it was kept, Fixed Deposits are similar to the lumpsum amount in mutual funds.