IPTV versus OTT
What is IPTV? A Complete Guide to Internet-Based Television
What is IPTV? Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) is a modern way of delivering television content through the internet, rather than traditional cable or satellite methods. With IPTV, subscribers can access live TV broadcasts or on-demand programs using an internet connection. Unlike conventional TV, which relies on broadcast signals or physical cables, IPTV streams video content directly over a broadband connection.
This digital television service is increasingly popular because it allows users to watch programs anytime and anywhere, as long as they have an internet connection. IPTV enables flexible viewing experiences, whether it’s live streaming or accessing a library of on-demand content.
How Does IPTV Work?
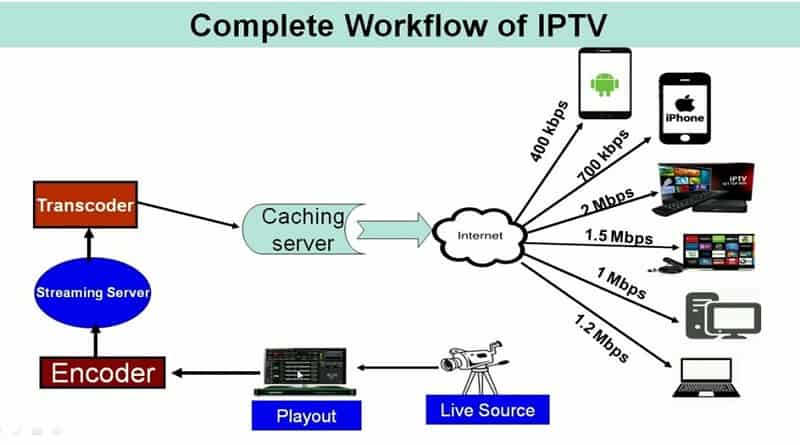
Understanding how IPTV works is key to grasping its advantages. The process is quite similar to how you browse the internet. IPTV uses the Internet Protocol (IP), the same system that delivers web content to your device, to stream video content. When a user selects a program or video to watch, IPTV divides the content into small data packets and delivers it over the internet.
These packets travel via high-speed fiber-optic cables to the user’s device. Once the packets reach the user’s home network, they are reassembled into the video content requested. This seamless process allows viewers to watch high-quality content without interruptions. IPTV is not only efficient but also highly customizable, offering personalized channels and services to suit individual preferences.
Why Choose IPTV Over Traditional TV?
The growing shift toward IPTV is largely due to its flexibility and wide-ranging content options. Users no longer have to wait for scheduled programming or rely on traditional set-top boxes. Instead, IPTV offers a more dynamic, interactive way to watch TV, where content is available on demand, and streaming quality remains high.
IPTV also supports a variety of devices—from smart TVs and laptops to smartphones and tablets—making it accessible no matter where you are.
What is OTT? Understanding Over-the-Top Streaming Services
What is OTT? The term “Over-the-Top” (OTT) refers to the delivery of video, audio, and other media content directly to viewers via the internet, bypassing traditional platforms like cable, satellite, and broadcast television. With OTT services, consumers can stream content anytime and on-demand without needing a conventional TV provider. This shift has revolutionized how people consume media, offering greater flexibility and control over what they watch.
OTT platforms, such as Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video, have become popular because they allow users to access content on various devices—smart TVs, smartphones, tablets, and computers. By cutting out traditional telecommunications and TV broadcasters, OTT puts the viewer in charge, delivering media directly over the internet.
How Does OTT Work?
OTT services work by streaming content through an internet connection. Users simply subscribe to an OTT platform, access its library of shows, movies, or music, and stream it directly over the internet, eliminating the need for traditional cable or satellite TV subscriptions. This direct-to-consumer approach gives OTT platforms the ability to offer vast libraries of content without the limitations of TV schedules.
Why Choose OTT Over Traditional TV?
OTT platforms are incredibly popular because of their flexibility and convenience. Users can choose from a variety of subscription options, access content anytime, and watch on multiple devices. This freedom to watch what you want, when you want, without being tied to a TV schedule is one of the biggest draws of OTT. Additionally, OTT services often offer exclusive content and original programming that can’t be found on traditional TV networks.

IPTV
Versatility in the network, programs foundation and program for end clients today are the real viewpoints prominent.
Calls for three driving fixings explicitly IP based associated TV and a substance material head and buying a bundle from the set-top box operator.
Their content transmits utilizing an individual framework of the ISP so they appear to resemble a TV administration more than spilling service
IPTV programs manage the TV channels to show the program thus there is a choice of chronicle just as replaying the projects at your own needs yet it is considerably less and you have to do it in the TV only..
IPTV requires total broadband web connectivity. OTT needs a general, open Internet.
IPTV supplies EPG (Electronic Program Guide) which happens to be an on-screen manual of ordinary transmitted programming television plans.
Closed, a proprietary network, accessed via a selected net service supplier
Expensive, Heavy investment in Bandwidth and infrastructure.
The high quality of service and quality of experience. Monitoring and control, interactive services
High quality, reliable network with management over the quality of services
IPTV services like U-Verse, Prism TV.
IPTV uses Transport Stream, transmission technology. Uses Real-time protocol over UDP, a connectionless protocol.
Multicast. Initial unicast burst throughout channel amendment resulting in Multicast be a part of
Premium content
TSP and IPTV platform vendors – Microsoft Mediaroom(currently Ericsson), ALU, Cisco.
Used primarily for premium VOD.
Uses a managed network.
Dedicated ecosystem.
OTT
No requirement for an administrator which appropriates content and is finished independently from anyone else.
Content is exhibited through the associated device making utilization of an unmanaged, open Internet arrange. Positively no outside apparatus like the set-top bundle is required.
They don’t have any network which is submitted and they are the administrators too with no unique foundation. The substance expands by means of any web association.
OTT providers manage creation houses and afterward live stream their shows on to the web for individuals to watch.
OTT needs a general, public Internet.
OTT program providers for the most part supply a list of visible substance material for guests to pick just as select from.
Delivered from content provider/aggregator to the viewer using an open network.
Low quality of service, the absence of live broadcast, non-premium content, unicast delivery model
Low cost, flexible model, Easy to manage and operate
Not guaranteed, works under best effort conditions
Popular Video on Demand services like YouTube, Netflix, Amazon LoveFilm, Hulu, Sky Go, BBC iPlayer etc.
Delivered over HTTP / TCP, a connected transport protocol. The movement towards adaptive streaming technologies HLS (Apple), Smooth Streaming (MS) and HDS (Adobe)
Unicast (HTTP), Simulated Multicast (UDP/TCP)
Freemium Content, the absence of DRM
OVP (Online Video Platforms) like Kaltura, Brightcove, Vlite(From Mobiotics), CDN Players like Akamai, L3, Limelight, Cloud Service Providers like Amazon
Used Primarily for Freemium VOD
Uses the unmanaged network.
Open ecosystem.


